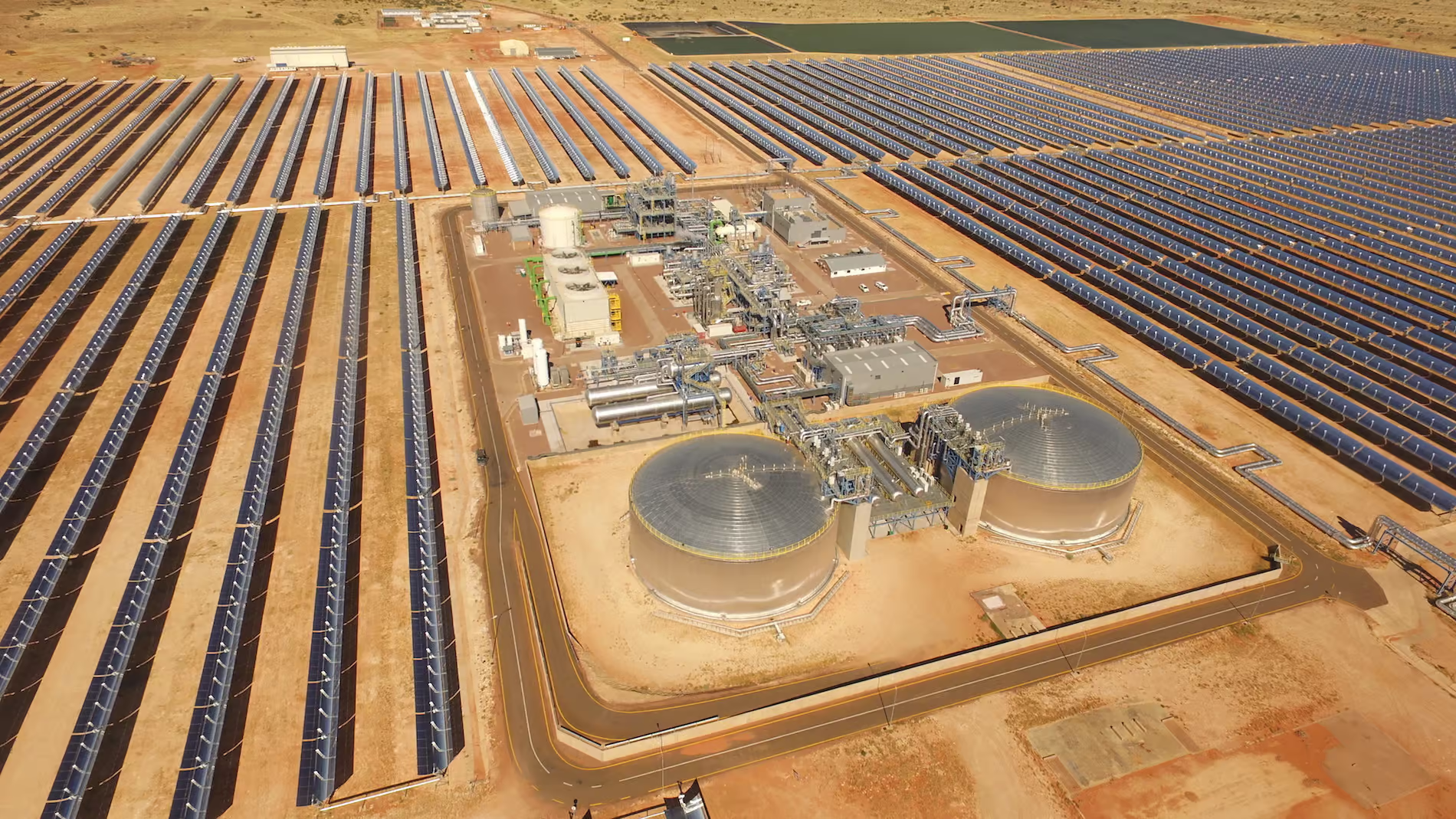
On April 8, 2025, Changzhou Royal Tech Solar Thermal Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as “Royal Tech”) successfully completed the production and shipment of a new generation of high-temperature vacuum molten salt collector tubes specially developed for the European Évora Advanced Trough Molten Salt Demonstration Project. As the most advanced demonstration project in Europe for third-generation trough solar thermal technology—characterized by large-aperture trough collectors and direct molten salt circulation—the Évora project fully adopts Royal Tech’s core collector tube components, marking China’s leading position in the global manufacturing of core solar thermal components.
Project Background: A Benchmark for EU Solar Thermal Technology Upgradation
The European Évora Advanced Trough Molten Salt Demonstration Project is jointly led by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and the University of Évora, Portugal, with funding from institutions including the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action and the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology. The project aims to demonstrate the operation of large-aperture trough collectors using molten salt as the heat transfer medium under 550°C heat collection conditions, providing economic data support for the large-scale deployment of solar thermal-photovoltaic hybrid power plants in Europe.

About the German Aerospace Center (DLR)
DLR, Germany’s national research institute for aerospace, energy, and transportation, manages R&D in aviation, space, energy, transportation, and security. As a global authority in solar thermal power, DLR has actively contributed to the R&D, demonstration, testing, and consulting of solar thermal technologies over the past decades, driving the industry’s global development.
Core Component Breakthrough: “Hardcore Strength” of Third-Generation Trough Technology Equipment
While Royal Tech’s high-temperature vacuum heat-transfer oil collector tubes have been widely exported to mainstream overseas projects, the molten salt vacuum collector tubes—critical components with the highest performance and quality requirements—are entering Europe’s most advanced third-generation trough solar thermal demonstration project for the first time. These products showcase the company’s technological and manufacturing advantages:

- New High-Temperature Absorption and Anti-Reflective Coatings: Capable of operating beyond 565°C, compatible with conventional binary molten salt and next-generation wide-temperature-range molten salt media. Features include higher transmittance and absorptance, lower emissivity, and optimized coating strategies for multi-temperature zones in collectors.
- Optimized Design for Molten Salt Vacuum Collector Tubes: High-temperature and corrosion-resistant materials, more efficient expansion absorption design to increase effective length, a vacuum maintenance system with a service life of over 35 years, and patented designs such as thermal shields and cosine reflectors for enhanced reliability and efficiency.
- Parallel Production Capacity for Multi-Specification Products: After receiving the order, cross-departmental collaboration quickly completed design reviews, process certifications, and type tests, adjusted production lines and equipment for flexible parallel production with 70mm heat-transfer oil standard tubes and 90mm heat-transfer oil collector tubes for Dubai’s 700MW solar thermal project, demonstrating Royal Tech’s strong capacity scheduling and support capabilities.
China’s Third-Generation Trough Solar Thermal Solutions Leading Global Cost Reduction and Technology Iteration
Since the commercialization of solar thermal power plants in the 1980s, the global market has grown steadily. Trough technology has evolved from first-generation medium-temperature heat-transfer oil systems (below 5.7m aperture, 50–100MW units) to second-generation high-temperature systems (8m aperture, 2.7 million m² heliostat fields, 200MW units, as seen in Dubai’s 3×200MW trough project), accounting for ~80% of the global market. Tower technology has advanced from first-generation direct steam generation (DSG, e.g., the 10MW Solar One in the U.S., 1982) to molten salt-based systems (e.g., the 10MW Solar Two in the U.S., 1996), with China achieving the greatest success over 30 years—Delingha’s 50MW molten salt tower plant remains the world’s only fully operational project of its kind.
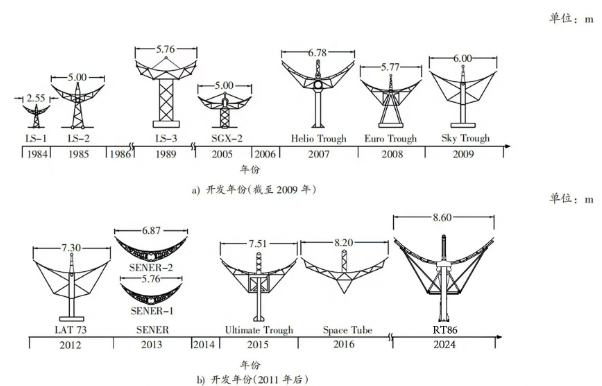
The third-generation trough technology, represented by CGN’s green low-carbon solar thermal demonstration project, features 8.6m large-aperture molten salt trough collectors, 2.6 million m² heliostat fields, and 300MW units. It significantly reduces power plant investment compared to the second generation while improving efficiency, driving substantial declines in levelized cost of electricity (LCOE). It retains trough technology’s advantages: high photoelectric efficiency, land conservation, reliable operation, simple control, strong climate adaptability, and easy maintenance.
From the perspective of the third-generation trough technology equipment supply chain, Chinese enterprises like CGN, Royal Tech, and Northwest Engineering Corporation of CEEC have made breakthroughs in large-aperture trough collector R&D. Royal Tech’s molten salt collector tubes have been mass-exported to Europe, and domestic molten salt tubes are widely used in Fresnel projects. CGN, Central South Engineering Corporation, and Royal Tech have also advanced in molten salt flexible connections, while localization of impedance heating, electric tracing, molten salt valves, pumps, and other equipment has been achieved. Supported by a complete industrial chain, China’s third-generation trough solutions are set to lead global solar thermal technology iteration and cost reduction.



