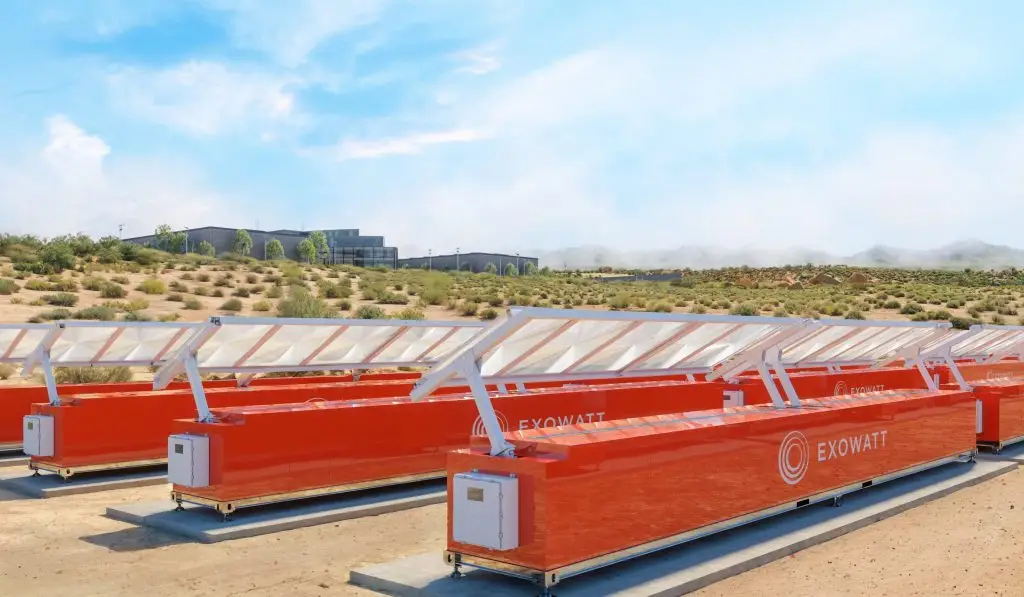
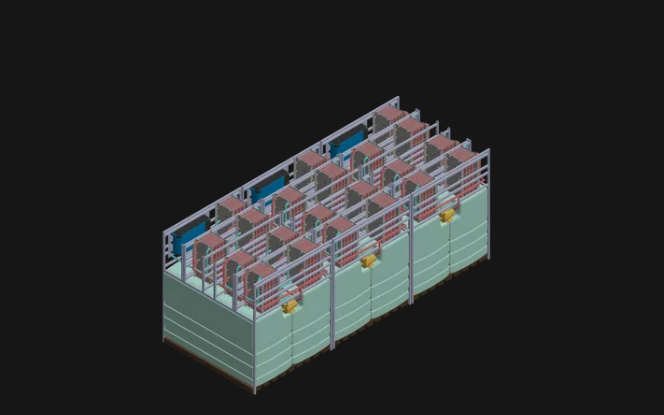
Exowatt is a company with an ambitious concept for powering AI data centers, backed by Sam Altman. The team is exploring the idea of using billions of hot stones as a foundational heat source for computing power.
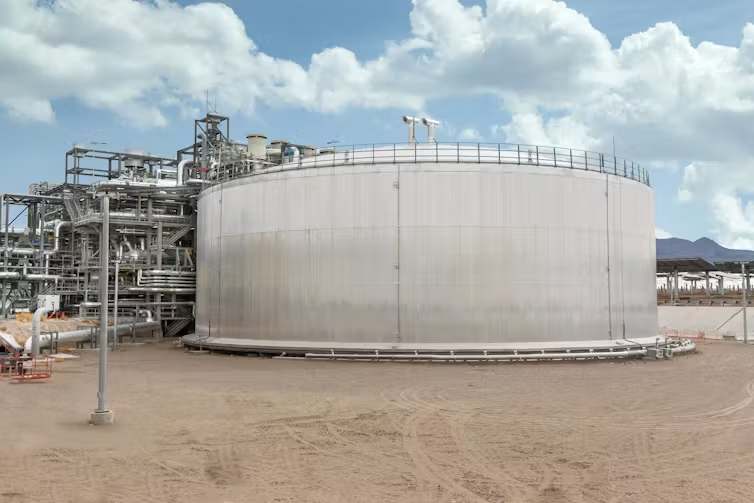
The core idea is to create a large thermal mass: the stones are heated to high temperatures and store the heat, which is then transferred through heat exchangers, triggering a steam-generation cycle to power data centers without excessive electricity drawn from the grid.
The advantages of this concept include potential stability of heat supply, reduced dependence on variable energy sources, and the ability to scale through modular blocks of stone storage. This approach could also reduce air emissions if the thermal energy is produced without burning fossil fuels.
However the path to implementation faces serious challenges: transporting and locating enormous quantities of stones, maintaining stable temperatures, efficient heat exchange, and the high capital cost of the project. There is also a need to address environmental issues, regulatory norms at sites, and safety of heat replenishment.
The availability of financial support from Sam Altman opens up opportunities for scientific research, partnerships with engineers, and platforms for pilot programs. The company aims to demonstrate the viability of this concept at early stages of development and move toward prototypes in the coming years.
How the concept will work in practice
In pilot projects, they will consider locating thermal masses near large data consumers or near geothermal resources where access to the necessary heat exists. The corresponding stone blocks can be housed in modular, space-efficient frames, enabling rapid scaling of the systems.
Heat transfer and the conversion of heat into electricity will require innovative heat exchangers and reliable cooling systems. It is also important to ensure long-term temperature stability with minimal energy losses.
Governments and regulators may require detailed environmental impact assessments, infrastructure development roadmaps, and safety verifications. Success depends on the ability to combine geological research, technical solutions, and the financial interests of stakeholders.