Macro Economic Forces Driving Critical Minerals Policy Evolution
Critical minerals policy frameworks are undergoing rapid transformation as governments worldwide recognise the strategic importance of securing supply chains for energy transition technologies. The intersection of decarbonisation objectives, geopolitical supply chain risks, and domestic economic development priorities creates complex policy environments where traditional mining royalty structures require fundamental reconsideration. Furthermore, the critical minerals transition necessitates sophisticated understanding of how fiscal policy can attract essential investment.
Australia’s position as holder of the world’s largest economic demonstrated vanadium resources places the nation at the centre of global energy storage supply chain discussions. This geological advantage, combined with established mining infrastructure and regulatory frameworks, positions Australian jurisdictions to leverage fiscal policy as a competitive tool for attracting critical minerals investment.
The evolution from variable to standardised royalty rates reflects broader mining industry evolution, where emerging technology sectors require the same regulatory certainty traditionally provided to established commodities. This policy convergence demonstrates sophisticated understanding of investment psychology in capital-intensive extractive industries.
Understanding the WA Vanadium Royalty Rate Structure
Implementation of the 2.5% Standardised Framework
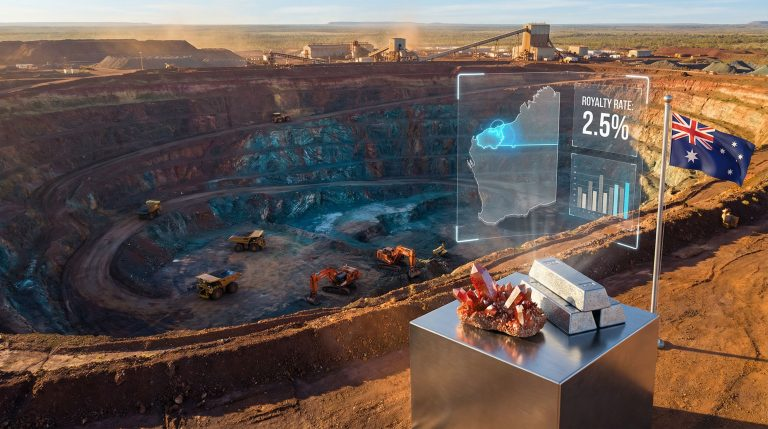
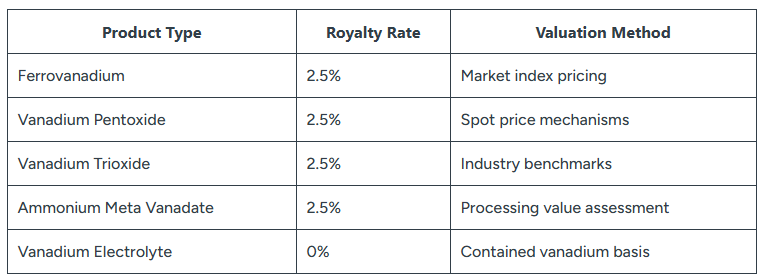
The Western Australian government’s implementation of a 2.5% flat royalty rate for vanadium products represents a significant shift from previous variable rate structures. This standardisation took effect in early February 2026, applying uniformly across all vanadium mining operations regardless of project scale or development stage. Consequently, the wa vanadium royalty rate provides unprecedented certainty for investors.
The new framework eliminates calculation complexity by establishing consistent rates across primary vanadium products while maintaining zero percent royalties for vanadium electrolyte production. This distinction creates clear fiscal incentives for downstream processing activities within Western Australia.
Vanadium Product Categories and Royalty Applications:
Regulatory Implementation Through Mining Amendment Regulations
The Mining (Royalties) Amendment Regulations 2026 provide the legal framework supporting this policy implementation. These regulations establish standardised calculation methodologies, reporting requirements, and compliance frameworks applicable across all Western Australian vanadium operations.
Transition arrangements accommodate existing mining leases while ensuring new applications benefit immediately from rate certainty. The regulatory framework includes dispute resolution mechanisms and audit procedures designed to maintain transparency and consistency in royalty assessments.
Comparative Analysis with Other Critical Minerals
Strategic Commodity Grouping Through Royalty Alignment
Western Australia’s decision to align vanadium with established commodities reflects strategic positioning within the critical minerals hierarchy. The 2.5% rate places vanadium alongside nickel, gold, and rare earths, distinguishing it from higher-rate commodities like lithium and copper concentrates at 5%.
This rate differentiation suggests government recognition of vanadium’s role in energy storage infrastructure versus traditional industrial applications. The alignment with gold and rare earths particularly indicates confidence in vanadium’s market maturity and production stability. Moreover, this aligns with recent developments including the US critical minerals order, which emphasises similar strategic thinking.
WA Critical Minerals Royalty Comparison:
- Vanadium, Nickel, Gold, Rare Earths: 2.5%
- Lithium Concentrate, Copper Concentrate: 5%
International Competitiveness Framework
The standardised rate enhances Western Australia’s competitive position relative to other major vanadium-producing jurisdictions. South Africa, China, and Russia maintain varying royalty and taxation structures that often lack the transparency and predictability provided by the WA framework.
This competitive positioning becomes particularly relevant as international buyers increasingly prioritise supply chain security and ESG compliance in sourcing decisions. Australia’s established regulatory environment combined with competitive fiscal terms creates advantages for long-term supply contracts.
Policy Development and Industry Consultation Process
Government Strategic Objectives and Election Commitments
The policy implementation fulfils explicit election commitments made by the Cook Labor Government, demonstrating political continuity in critical minerals development strategies. The timing reflects recognition that the vanadium sector had reached a development stage requiring regulatory certainty to attract significant capital investment.
Government statements emphasise alignment with broader energy transition objectives, particularly as Western Australia phases out coal-fired power generation. Long-duration energy storage becomes critical infrastructure for grid stability as renewable energy penetration increases.
Industry Advocacy and Consultation Outcomes
The Association of Mining and Exploration Companies conducted sustained advocacy over two years preceding the policy announcement. According to the WA government announcement, industry concerns centred on three key areas:
- Rate certainty: Elimination of variable calculation methodologies
- Value chain consistency: Alignment across extraction and processing activities
- Downstream incentives: Encouragement of value-add manufacturing within the state
The final policy directly addresses each concern through the standardised 2.5% rate, consistent application across the value chain, and zero-rate incentives for electrolyte production. This outcome demonstrates effective industry-government collaboration in policy development.
Warren Pearce, CEO of the Association of Mining and Exploration Companies, noted that the policy reform sends a positive message to investors that Western Australia understands commercial realities facing critical mineral developers and is prepared to adapt frameworks supporting emerging industries.
Economic Implications for Vanadium Project Development
Project Viability and Investment Certainty Enhancement
Vanadium mining operations typically operate on 15-20% EBITDA margins, making royalty rate predictability financially significant for project economics. The transition from variable to fixed percentage rates enables precise financial modelling over typical 20-year project lifespans.
The standardised framework provides three distinct advantages:
- Financial modelling precision through fixed percentage calculations
- Comparative investment analysis via alignment with established commodity rates
- Downstream processing incentives through zero-rate electrolyte production
Capital-intensive vanadium processing infrastructure requires 10-15 year payback periods, necessitating regulatory certainty for investment justification. The policy eliminates a significant source of financial modelling uncertainty that previously constrained project development.
Regional Economic Development and Employment Multiplier Effects
Remote vanadium mining operations generate employment multiplier effects through supply chain requirements, accommodation facilities, and professional services. Regional mining operations typically create 3-5 times direct employment through supporting economic activities.
The Gabanintha Project near Meekatharra exemplifies these regional development benefits. The project’s location within established mining infrastructure reduces capital expenditure requirements while maximising regional employment outcomes.
Government regional development grant programmes coordinate with mining project development to amplify economic benefits. This integrated approach maximises public investment returns while supporting private sector development objectives.
Integration with Western Australia’s Energy Storage Strategy
Vanadium Battery Manufacturing and Grid Infrastructure
The zero percent royalty rate for vanadium electrolyte production creates direct fiscal incentives for establishing battery manufacturing facilities within Western Australia. This policy aligns with plans for Australia’s first locally built utility-scale vanadium battery installation in Kalgoorlie. Additionally, these developments support broader renewable energy solutions across the mining sector.
Vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) provide long-duration energy storage capabilities essential for grid stability as coal-fired baseload capacity is retired. The technology’s scalability and longevity make it particularly suitable for utility-scale applications.
Key Advantages of Vanadium Battery Technology:
- Long duration storage: 4-12 hour discharge capabilities
- Cycle longevity: 20+ year operational lifespan
- Scalability: Modular design enabling capacity expansion
- Safety profile: Non-flammable electrolyte chemistry
Supply Chain Development and Value-Add Manufacturing
The policy framework encourages development of integrated supply chains from raw material extraction through finished battery component manufacturing. Zero royalties on electrolyte production provide cost advantages for establishing manufacturing facilities within the state.
Regional manufacturing hubs could leverage existing mining services infrastructure while creating higher-value employment opportunities. Technology transfer and skills development programmes support workforce transition from traditional mining to advanced manufacturing roles.
Export market positioning becomes enhanced through value-add manufacturing capabilities. Finished electrolyte products command premium pricing compared to raw vanadium concentrates, improving overall industry profitability.
Implementation Requirements and Compliance Framework
Administrative and Regulatory Coordination
The Mining (Royalties) Amendment Regulations 2026 establish comprehensive administrative frameworks for royalty calculation, assessment, and collection. These regulations coordinate with existing mining approval processes to minimise administrative burden on operators.
Key Implementation Components:
- Standardised calculation methodologies for all vanadium products
- Quarterly reporting requirements aligned with production cycles
- Audit and verification procedures for royalty assessments
- Appeals processes for disputed calculations
Integration with federal regulatory frameworks ensures consistency across jurisdictional boundaries. Coordination between state and commonwealth agencies reduces regulatory complexity for multi-jurisdictional operations.
Transition Mechanisms and Legacy Arrangements
Existing mining operations transition from previous variable rate structures without penalty or administrative complexity. The February 2026 implementation date provides clear demarcation for calculation purposes while maintaining operational continuity.
New mining applications benefit immediately from rate certainty, enabling improved financial modelling and investment decision-making. This immediate application demonstrates government commitment to supporting sector development.
Global Market Positioning and Strategic Implications
Australia’s Resource Endowment and Competitive Advantages
Australia’s position as holder of the world’s largest economic demonstrated vanadium resources provides significant competitive advantages in global markets. This geological endowment, combined with established mining expertise and infrastructure, creates natural supply security for international buyers.
The standardised royalty framework enhances these natural advantages through regulatory predictability and cost competitiveness. International mining companies can make capital allocation decisions with greater confidence regarding long-term operational costs.
Australia’s Global Vanadium Position:
- Largest economic demonstrated resources globally
- Established mining infrastructure and expertise
- Stable regulatory and political environment
- Proximity to Asian manufacturing markets
Investment Flow Implications and Capital Market Access
The policy announcement has direct implications for foreign direct investment flows into the Western Australian vanadium sector. Standardised rates reduce investment risk premiums typically applied to jurisdictions with variable or uncertain fiscal regimes. However, successful implementation requires understanding of modern investment strategies that consider both regulatory certainty and market dynamics.
International mining companies increasingly incorporate ESG factors and supply chain security considerations into investment decisions. Australia’s transparent regulatory framework and democratic governance provide advantages over alternative producing jurisdictions.
Capital market access improves through enhanced project bankability. Mining projects with predictable fiscal frameworks typically access debt financing at more favourable terms, improving overall project returns.
Long-term Strategic Benefits for Western Australia
Economic Diversification and Sectoral Development
The vanadium sector development contributes to Western Australia’s economic diversification beyond traditional iron ore and gold mining. Critical minerals extraction and processing create new employment categories while leveraging existing geological and infrastructure advantages.
Regional economic development outcomes extend beyond direct mining employment through supply chain multiplier effects. Professional services, logistics, and support industries benefit from expanded mining activity in remote areas.
Export revenue diversification reduces economic dependence on traditional commodity cycles. Vanadium’s role in energy storage applications provides exposure to growing renewable energy markets rather than declining fossil fuel sectors.
Technology Leadership and Innovation Ecosystem Development
Western Australia’s positioning in vanadium battery manufacturing creates opportunities for technology leadership in energy storage applications. Research and development collaboration between mining companies, technology providers, and educational institutions supports innovation ecosystem development.
Skills development programmes prepare regional workforces for advanced manufacturing roles associated with battery production. These programmes leverage existing mining expertise while developing new technical capabilities relevant to energy storage technologies.
International partnership opportunities emerge through technology leadership positioning. Joint ventures with international battery manufacturers could establish Western Australia as a global hub for vanadium battery production and development.
Regulatory Framework Analysis and Future Considerations
Policy Integration with Broader Energy Transition Objectives
The vanadium royalty framework demonstrates sophisticated policy integration across multiple government priorities. Energy transition support, regional development, and critical minerals security objectives align through coordinated fiscal incentives.
Coal-fired power station phase-out creates direct demand for long-duration energy storage technologies. Government recognition of this demand-supply relationship influences fiscal policy design to support domestic manufacturing capabilities.
According to industry analysis, the policy changes signal strong government support for new vanadium projects, providing essential certainty for developers and investors alike.
What Future Policy Developments Might We Expect?
The success of the vanadium royalty framework may influence policy development for other critical minerals. Standardised rates and downstream processing incentives could extend to additional commodities as sectors mature and investment requirements evolve.
International trade considerations may require policy adjustments as global critical minerals markets develop. Bilateral trade agreements and multilateral frameworks could influence future royalty rate structures and calculation methodologies.
Environmental and social governance requirements continue evolving, potentially requiring integration with royalty frameworks. Carbon pricing mechanisms and biodiversity offset requirements may influence future policy design.
The Western Australian vanadium royalty framework represents a comprehensive approach to critical minerals policy development, successfully balancing revenue generation objectives with industry development priorities. The wa vanadium royalty rate of 2.5% provides essential investment certainty while positioning the state competitively for long-term sectoral growth.
This regulatory approach serves as a potential model for other jurisdictions developing critical minerals sectors while maintaining competitive investment environments. The emphasis on industry consultation, long-term strategic planning, and policy integration across multiple government objectives demonstrates sophisticated policy development practices suitable for complex emerging industries.
Want to Stay Ahead of Critical Minerals Investment Opportunities?
Discovery Alert’s proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers instant notifications on significant ASX mineral discoveries, including emerging vanadium and critical minerals opportunities that could benefit from policy changes like Western Australia’s new royalty framework. Explore historic examples of exceptional discovery returns and begin your 14-day free trial today to position yourself ahead of market movements in this rapidly evolving sector.